Outlier detection
An outlier is a data point that is significantly different from the rest of the data. Presence of outliers in training data can deteriorate the generalization performance of machine learning models. In this aspect, we aim to remove outliers from signals.
- signal.process_outliers(strategy='residual', threshold=None, above_threshold=False, output_scores=False, impute=False)
This method processes a signal and removes or imputes outliers.
- Parameters:
signal – The signal to process.
strategy – Two strategies are available: 1,
residual: it looks at residuals from a time series model to detect an outlier. 2,modified_zscore: it looks at modified z-scores to detect an outlier.threshold – It acts as a threshold on the decision scores for outliers above which a data point is flagged as an outlier. The default threshold is strategy-dependent: 3 for
residualand 3.5 formodified_zscore.above_threshold – If set to True, outputs when the scores are above the threshold, instead of below. This means only the outliers are kept and other values removed.
output_scores – If set to True, outputs the z-scores instead of the data values.
impute – If set to True, the missing values are imputed with the expected value, instead of being removed. This setting cannot be combined with above_threshold or output_scores.
Methodology
The method calculates a score for each data point based on the chosen strategy. Any point with an absolute score value greater than the threshold is considered an outlier.
Residual strategy:
The residual strategy detects outliers by first fitting a time series model with trend and seasonal components to the signal, and then working with the model residuals. This strategy uses Unobserved Components Model.
The residuals from the model estimation are assumed to be normally distributed with a mean of zero. The standard deviation of the residuals is used to calculate Z-scores for each point.
Modified Z-score strategy:
Mathematically, the Modified Z-score is calculated as:
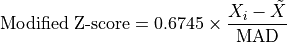
where 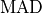 is the median of the absolute deviations,
is the median of the absolute deviations, 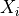 is the i-th value in
the signal, and
is the i-th value in
the signal, and 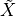 is the median of the signal. The 0.6745 constant is applied to
scale the modified z-score to be comparable to the standard z-score.
is the median of the signal. The 0.6745 constant is applied to
scale the modified z-score to be comparable to the standard z-score.
Examples:
To process outliers in sales signal, call:
fs_actual('sales').process_outliers()
To specify a particular threshold, we can use:
fs_actual('sales').process_outliers(threshold=3)
To specify a particular strategy, we can use:
fs_actual('sales').process_outliers(strategy='modified_zscore', threshold=3.5)